It’s about the data struct of linear — queue and the Algorithm on it.
Table of contents
Open Table of contents
队列(queue) && 双端队列(deque)
Last in - Last out First in - First out
队列的关键点
- 队列本质是定义了一组先进先出的接口规范,可以有不同的实现
- 在线性结构头部和尾部进行排队操作的,可以联想到使用队列进行解决
- 队列的变种比较丰富,需要能够熟练掌握诸如双端队列,优先队列等高频接口的实现
操作复杂度
- 入队 O(1) (队列尾部插入,双端队列支持头部插入)
- 出队 O(1)(队列头部弹出,双端队列支持尾部弹出)
- 访问 O(1) (访问队头,双端队列可以同时访问队头和队尾)
优先队列(priority queue)
优先队列的关键点
- 普通队列的优先级是基于“时间”,即先进的,“时间”优先级比较高,先出
- 优先队列则是相当于普通队列的泛化版本,可以自己定义以及实现“优先级”
- 优先队列只是一组按照自定义优先级出队的接口规范,底层可以基于二叉堆,二叉平衡树等等不同的实现
操作复杂度
- 访问最值(访问优先级最高的元素,但是不取)O(1)
- 插入元素,常见的实现是 O(logN)(某些高级的数据结构,可以做到 O(1))
- 取最值 O(logN)(取出后最值元素后,还需要的维护开销)
Note: 插入:一般是 O(logN)(二叉堆),一些高级数据结构可以做到 O(1)(配对堆,斐波那契堆)
Java JDK
- Queue,Deque 可以用 LinkedList 实现
- PrioriyQueue
实战
- Implement Stack using Queues
Implement a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack using only two queues. The implemented stack should support all the functions of a normal stack (push, top, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyStack class:
- void push(int x) Pushes element x to the top of the stack.
- int pop() Removes the element on the top of the stack and returns it.
- int top() Returns the element on the top of the stack.
- boolean empty() Returns true if the stack is empty, false otherwise.
Notes:
- You must use only standard operations of a queue, which means that only push to back, peek/pop from front, size and is empty operations are valid.
- Depending on your language, the queue may not be supported natively. You may simulate a queue using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a queue’s standard operations.
Example 1:
Input
["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
Output
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]
Explanation
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // return 2
myStack.pop(); // return 2
myStack.empty(); // return FalseConstraints:
- 1 <= x <= 9
- At most 100 calls will be made to push, pop, top, and empty.
- All the calls to pop and top are valid.
Follow-up: Can you implement the stack using only one queue?
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList();
queue2 = new LinkedList();
}
public void push(int x) {
queue2.offer(x);
while(!queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
Queue<Integer> temp = queue2;
queue2 = queue1;
queue1 = temp;
}
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
思路
- 定义两个队列
- push 的时候,先从 queue2 入队,如果 queue1 不为空,将 queue1 的出队,queue2 入队
- top 和 peek 都只需要从 queue1.
- Design Circular Queue
Design your implementation of the circular queue. The circular queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle, and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called “Ring Buffer”.
One of the benefits of the circular queue is that we can make use of the spaces in front of the queue. In a normal queue, once the queue becomes full, we cannot insert the next element even if there is a space in front of the queue. But using the circular queue, we can use the space to store new values.
Implement the MyCircularQueue class:
- MyCircularQueue(k) Initializes the object with the size of the queue to be k.
- int Front() Gets the front item from the queue. If the queue is empty, return -1.
- int Rear() Gets the last item from the queue. If the queue is empty, return -1.
- boolean enQueue(int value) Inserts an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful.
- boolean deQueue() Deletes an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful.
- boolean isEmpty() Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not.
- boolean isFull() Checks whether the circular queue is full or not.
- You must solve the problem without using the built-in queue data structure in your programming language.
Example 1:
Input
["MyCircularQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "Rear", "isFull", "deQueue", "enQueue", "Rear"]
[[3], [1], [2], [3], [4], [], [], [], [4], []]
Output
[null, true, true, true, false, 3, true, true, true, 4]
Explanation
MyCircularQueue myCircularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3);
myCircularQueue.enQueue(1); // return True
myCircularQueue.enQueue(2); // return True
myCircularQueue.enQueue(3); // return True
myCircularQueue.enQueue(4); // return False
myCircularQueue.Rear(); // return 3
myCircularQueue.isFull(); // return True
myCircularQueue.deQueue(); // return True
myCircularQueue.enQueue(4); // return True
myCircularQueue.Rear(); // return 4Constraints:
- 1 <= k <= 1000
- 0 <= value <= 1000
- At most 3000 calls will be made to enQueue, deQueue, Front, Rear, isEmpty, and isFull.
class MyCircularQueue {
private int capacity;
private int[] element;
private int front;
private int rear;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
capacity = k+1;
element = new int[capacity];
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
element[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return element[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return element[(rear - 1 + capacity)%capacity];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1)% capacity == front;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/思路:
我们可以通过一个数组进行模拟,通过操作数组的索引构建一个虚拟的首尾相连的环。在循环队列结构中,设置一个队尾 rear 与队首 front,且大小固定,结构如下图所示:
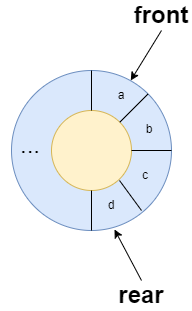
在循环队列中,当队列为空,可知 front=rear;而当所有队列空间全占满时,也有 front=rear。为了区别这两种情况,假设队列使用的数组有 capacity 个存储空间,则此时规定循环队列最多只能有 capacity−1 个队列元素,当循环队列中只剩下一个空存储单元时,则表示队列已满。根据以上可知,队列判空的条件是 front=rear,而队列判满的条件是front=(rear+1)%capacity。
对于一个固定大小的数组,只要知道队尾 rear 与队首 front,即可计算出队列当前的长度:(rear−front+capacity)%capacity。
循环队列的属性如下:
- elements:一个固定大小的数组,用于保存循环队列的元素。
- capacity:循环队列的容量,即队列中最多可以容纳的元素数量。
- front:队列首元素对应的数组的索引。
- rear:队列尾元素对应的索引的下一个索引。
循环队列的接口方法如下:
- MyCircularQueue(int k): 初始化队列,同时 base 数组的空间初始化大小为 k+1。front,rear 全部初始化为 0
- enQueue(int value):在队列的尾部插入一个元素,并同时将队尾的索引 rear 更新为
(rear+1)%capacity。 - deQueue():从队首取出一个元素,并同时将队首的索引 front 更新为
(front+1)%capacity。 - Front():返回队首的元素,需要检测队列是否为空。
- Rear():返回队尾的元素,需要检测队列是否为空。
- isEmpty():检测队列是否为空,根据之前的定义只需判断 rear 是否等于 front。
- isFull():检测队列是否已满,根据之前的定义只需判断 front 是否等于
(rear+1)%capacity。
- Design Circular Deque
Design your implementation of the circular double-ended queue (deque).
Implement the MyCircularDeque class:
- MyCircularDeque(int k) Initializes the deque with a maximum size of k.
- boolean insertFront() Adds an item at the front of Deque. Returns true if the operation is successful, or false otherwise.
- boolean insertLast() Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Returns true if the operation is successful, or false otherwise.
- boolean deleteFront() Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Returns true if the operation is successful, or false otherwise.
- boolean deleteLast() Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Returns true if the operation is successful, or false otherwise.
- int getFront() Returns the front item from the Deque. Returns -1 if the deque is empty.
- int getRear() Returns the last item from Deque. Returns -1 if the deque is empty.
- boolean isEmpty() Returns true if the deque is empty, or false otherwise.
- boolean isFull() Returns true if the deque is full, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input
["MyCircularDeque", "insertLast", "insertLast", "insertFront", "insertFront", "getRear", "isFull", "deleteLast", "insertFront", "getFront"]
[[3], [1], [2], [3], [4], [], [], [], [4], []]
Output
[null, true, true, true, false, 2, true, true, true, 4]
Explanation
MyCircularDeque myCircularDeque = new MyCircularDeque(3);
myCircularDeque.insertLast(1); // return True
myCircularDeque.insertLast(2); // return True
myCircularDeque.insertFront(3); // return True
myCircularDeque.insertFront(4); // return False, the queue is full.
myCircularDeque.getRear(); // return 2
myCircularDeque.isFull(); // return True
myCircularDeque.deleteLast(); // return True
myCircularDeque.insertFront(4); // return True
myCircularDeque.getFront(); // return 4Constraints:
- 1 <= k <= 1000
- 0 <= value <= 1000
- At most 2000 calls will be made to insertFront, insertLast, deleteFront, deleteLast, getFront, getRear, isEmpty, isFull.
class MyCircularDeque {
// 1、不用设计成动态数组,使用静态数组即可
// 2、设计 head 和 tail 指针变量
// 3、head == tail 成立的时候表示队列为空
// 4、tail + 1 == head
private int capacity;
private int[] arr;
private int front;
private int rear;
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
capacity = k+1;
arr = new int[capacity];
// 头部指向第 1 个存放元素的位置
// 插入时,先减,再赋值
// 删除时,索引 +1(注意取模)
front = 0;
// 尾部指向下一个插入元素的位置
// 插入时,先赋值,再加
// 删除时,索引 -1(注意取模)
rear = 0;
}
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
front = (front -1 + capacity) % capacity;
arr[front] = value;
return true;
}
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
arr[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
public boolean deleteFront() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
// front 被设计在数组的开头,所以是 +1
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
public boolean deleteLast() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
// 被设计在数组的末尾,所以是 -1
rear = (rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity;
return true;
}
public int getFront() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return arr[front];
}
public int getRear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
// 当 rear 为 0 时防止数组越界
return arr[(rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return front == rear;
}
public boolean isFull(){
// 注意:这个设计是非常经典的做法
return (rear + 1) % capacity == front;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularDeque object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularDeque obj = new MyCircularDeque(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.insertFront(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.insertLast(value);
* boolean param_3 = obj.deleteFront();
* boolean param_4 = obj.deleteLast();
* int param_5 = obj.getFront();
* int param_6 = obj.getRear();
* boolean param_7 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_8 = obj.isFull();
*/思路:
根据循环队列的定义,队列判空的条件是 front=rear,而队列判满的条件是front=(rear+1)%capacity,对于一个固定大小的数组,只要知道队尾 rear与队首front,即可计算出队列当前的长度:(rear−front+capacity)%capacity.循环双端队列与循环队列的属性一致:
- elements:一个固定大小的数组,用于保存循环队列的元素。
- capacity:循环队列的容量,即队列中最多可以容纳的元素数量。
- front:队列首元素对应的数组的索引。
- rear:队列尾元素对应的索引的下一个索引。
循环双端队列的接口方法如下:
- MyCircularDeque(int k):初始化队列,同时 base 数组的空间初始化大小为 k+1。front,rear 全部初始化为 0。
- insertFront(int value):队列未满时,在队首插入一个元素。我们首先将队首 front 移动一个位置,更新队首索引为 front 更新为
(front−1+capacity)%capacity。 - insertLast(int value):队列未满时,在队列的尾部插入一个元素,并同时将队尾的索引 rear 更新为
(rear+1)%capacity。 - deleteFront():队列不为空时,从队首删除一个元素,并同时将队首的索引 front 更新为
(front+1)%capacity。 - deleteLast():队列不为空时,从队尾删除一个元素。并同时将队尾的索引 rear 更新为
(rear−1+capacity)%capacity。 - getFront():返回队首的元素,需要检测队列是否为空。
- getRear():返回队尾的元素,需要检测队列是否为空。
- isEmpty():检测队列是否为空,根据之前的定义只需判断 rear 是否等于 front。
- isFull():检测队列是否已满,根据之前的定义只需判断 front 是否等于
(rear+1)%capacity。